Abstract
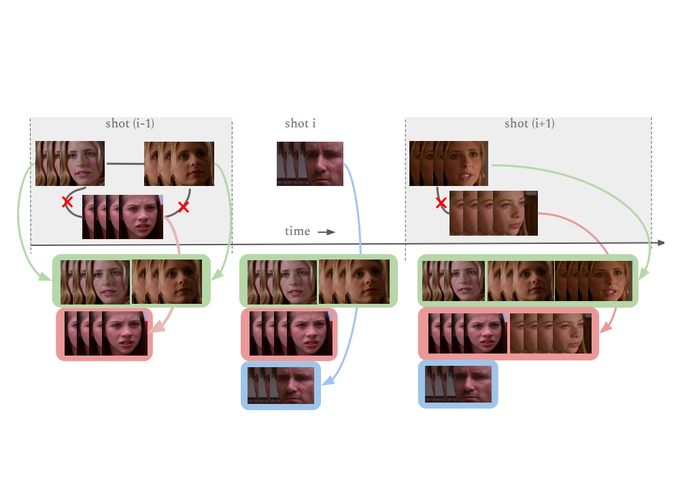
We address the problem of face clustering in long, real world videos. This is a challenging task because faces in such videos exhibit wide variability in scale, pose, illumination, expressions, and may also be partially occluded. The majority of the existing face clustering algorithms are offline, i.e., they assume the availability of the entire data at once. However, in many practical scenarios, complete data may not be available at the same time or may be too large to process or may exhibit significant variation in the data distribution over time. We propose an online clustering algorithm that processes data sequentially in short segments of variable length. The faces detected in each segment are either assigned to an existing cluster or are used to create a new one. Our algorithm uses several spatiotemporal constraints, and a convolutional neural network (CNN) to obtain a robust representation of the faces in order to achieve high clustering accuracy on two benchmark video databases (82.1% and 93.8%). Despite being an online method (usually known to have lower accuracy), our algorithm achieves comparable or better results than state-of-the-art offline and online methods.